Confused about retinol vs retinaldehyde? This article compares their effectiveness, potency, and skin tolerance to help you determine which is best for you.
Introduction to Retinoids
Retinoids are a powerhouse group of skincare ingredients derived from vitamin A, celebrated for their remarkable anti-aging benefits and ability to transform skin. By boosting cell turnover and stimulating collagen production, retinoids help improve skin texture, reduce fine lines and wrinkles, and address a variety of skin concerns. Whether you’re dealing with acne-prone skin, mature skin, or want to maintain a youthful complexion, retinoids can make a noticeable difference.
These ingredients come in several forms, each with its level of potency and potential for skin irritation. From gentle options suitable for sensitive skin to more robust formulas for those seeking dramatic results, understanding the different types of retinoids is key to finding the right fit for your skin type and goals. With regular use, retinoids can help smooth fine lines, enhance skin radiance, and support healthy, resilient skin.
Key Takeaways
- Retinaldehyde is more effective than retinol, requiring only one conversion step to deliver results, making it a quicker option for improved skin texture and tone.
- Both retinol and retinaldehyde can cause irritation, but retinaldehyde is better tolerated, especially for sensitive skin, and is effective for acne-prone skin.
- Using retinoids consistently can lead to significant skin improvements within a few weeks, with long-term benefits visible after at least 6 months of regular use.
- Both retinol and retinaldehyde have clinically proven benefits for improving skin texture and reducing visible signs of aging.

Understanding Retinol and Retinaldehyde
Retinol and retinal are two powerful forms of vitamin A that have revolutionized the skincare industry. These retinoids and other retinoids are celebrated for their ability to enhance cell turnover, improve skin texture, and stimulate collagen production, making them essential for anyone looking to achieve healthier, more youthful skin. Additionally, skin cell turnover plays a crucial role in this process.
While both retinol and retinaldehyde belong to the retinoid family, their effectiveness and the way they interact with the skin can differ significantly. Knowing these differences helps in selecting the right retinoid for your skincare needs. The effects of retinol and retinaldehyde on skin are compared and show differences in texture improvement, appearance, and potential irritation levels.
What is Retinol?
Retinol, a form of vitamin A, is renowned for its ability to promote skin cell renewal and combat signs of aging. This potent ingredient works by regulating cell turnover, which helps to smooth fine lines and prevent acne. However, before retinol can exert its effects on the skin, it must undergo a two-step conversion process to become retinoic acid, the active form that interacts with skin cells. Additionally, Retin-A is often discussed in relation to these benefits.
Retinol is suitable for a broad range of skin types, particularly beneficial for those in their late 20s to 40s who are beginning to see the early signs of aging. Its versatility makes it a popular choice in many anti-aging and skin-renewing products. Retinol is also effective in addressing uneven skin tone, helping to create a more uniform complexion.
What is Retinaldehyde?
Retinaldehyde, another potent form of vitamin A, stands out for its proximity to all trans retinoic acid. Unlike retinol, retinaldehyde requires only one conversion step to become pure retinoic acid, making it a more effective and quicker-acting option. This closer proximity allows retinaldehyde to deliver faster results in improving skin texture and tone, showcasing its active form of vitamin A.
Not only is retinaldehyde more potent, but it also tends to cause less irritation compared to retinol, making it a preferred choice for normal to oily skin types looking for significant anti-aging benefits without the discomfort.
Retinyl Esters and Other Forms of Retinoids
Retinyl esters are the mildest form of vitamin A used in skincare products, making them a gentle introduction to the retinoid family. Because they require several conversion steps before becoming retinoic acid, the active form that delivers visible results, they are less likely to irritate, making them ideal for sensitive skin or those new to retinoids. You’ll often find retinyl esters in over-the-counter creams and serums designed to improve skin texture and provide subtle anti-aging benefits.

For those seeking more noticeable improvements in uneven skin texture, fine lines and wrinkles, or treating acne, more potent forms like retinol and retinaldehyde are available. These require fewer conversion steps to reach the active form of vitamin A, making them more effective at improving skin texture and reducing the appearance of fine lines. Retinaldehyde, in particular, stands out as a potent form that delivers faster results for those looking to address multiple skin concerns with a single ingredient.
Comparing Potency and Effectiveness
When it comes to potency and effectiveness, retinaldehyde often takes the lead. Acting up to eleven times faster than retinol, retinaldehyde is recognized for its ability to deliver quicker improvements in skin texture and tone. This makes it an attractive option for those looking for more immediate results.
While retinaldehyde is the most potent over-the-counter option, prescription strength retinoid products like tretinoin offer even greater potency but come with a higher risk of irritation. The potency of these retinoids is a critical factor in their effectiveness. Knowing the differences in their strength can guide you in choosing the right product for your more potent retinoid skin concerns.
Potency Levels
Retinaldehyde is considered the most potent retinoid available over the counter. Its proximity to retinoic acid, just one conversion step away, means it can deliver faster and more significant results compared to retinol, which is two steps removed. This makes retinaldehyde a preferred choice for those seeking rapid improvements in skin health and appearance.
The higher potency of retinaldehyde translates to a more effective treatment with potentially less irritation, making it a powerful option for those serious about their skincare routine and retinal serums. Additionally, some products like adapalene are classified as synthetic retinoids and are known for their effectiveness in treating acne and signs of aging.
Skin Benefits
Both retinol and retinaldehyde offer a myriad of benefits for the skin. Retinol is known for enhancing skin texture, promoting radiance, and improving overall skin appearance. On the other hand, retinaldehyde is particularly effective for treating advanced acne and reducing visible wrinkles due to its potent action on the skin.
Both retinol and retinaldehyde can also help fade dark spots and hyperpigmentation, leading to a more even skin tone. Retinaldehyde’s ability to unclog pores and balance oil production makes it an excellent choice for managing acne breakouts and acne-prone skin, while its faster action is ideal for targeting deep wrinkles and established signs of aging.
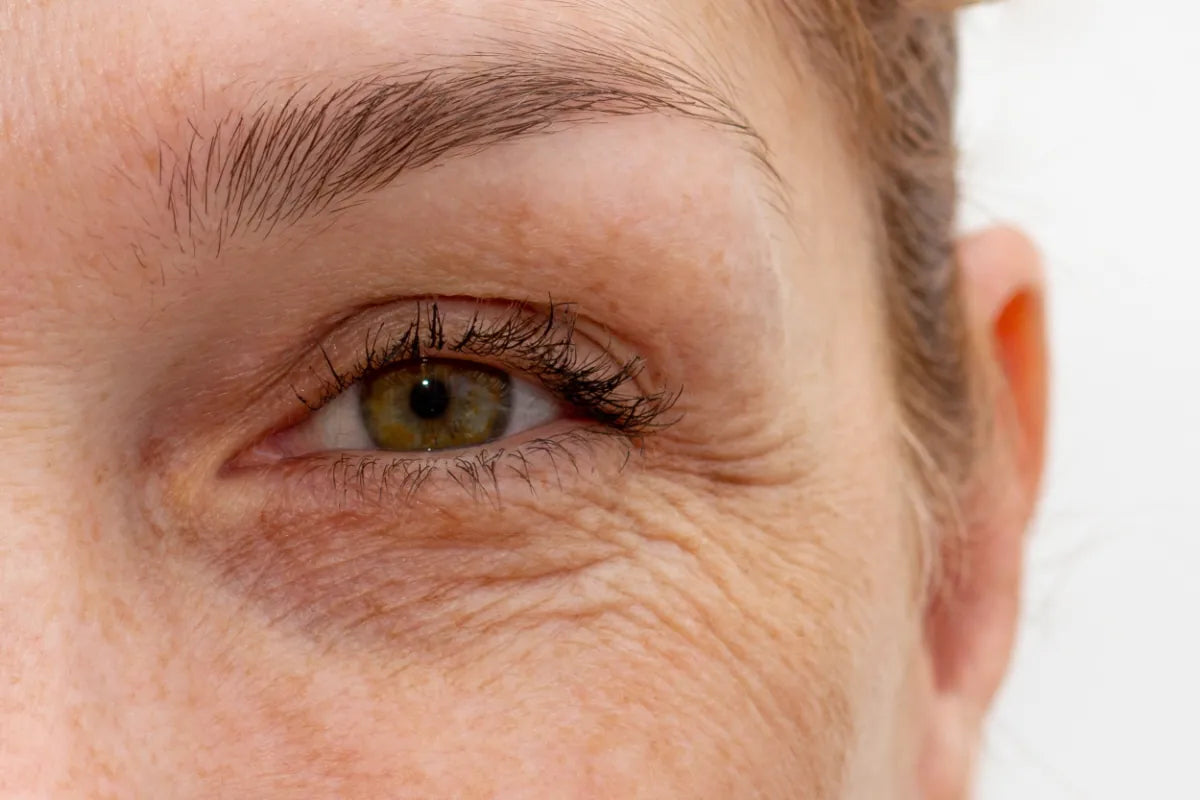
Skin Tolerance and Irritation Potential
One of the critical factors in choosing a retinoid is how well your skin can tolerate it. It is crucial to select a retinoid that matches your skin's tolerance to minimize irritation and ensure comfort. While both retinol and retinaldehyde can cause temporary reactions like dryness and peeling, retinaldehyde is often better tolerated, especially by those with sensitive skin. Knowing these potential reactions can help you manage them effectively.
Different skin types react differently to retinoid receptors, and being aware of these reactions and the skin’s tolerance is crucial for effective and safe skincare products to maintain a healthy skin barrier.

Sensitive Skin
For individuals with sensitive skin, retinaldehyde is often a better option because:
- It tends to induce less burning and peeling compared to retinol and tretinoin.
- It is a more suitable choice for those with delicate skin.
- While retinol can be irritating and cause peeling, especially in sensitive skin, retinaldehyde offers rapid improvements with better tolerability.
- Retinaldehyde’s lower irritation potential enhances its safety profile, making it a gentler yet practical option for those with sensitive skin, minimizing potential irritation.
Initial Reactions
Both retinol and retinaldehyde can cause initial reactions such as dryness, redness, and peeling, as well as skin irritation, when first introduced to the skin. These reactions are typically temporary and can be managed by gradually introducing the retinoid into your skincare routine. Begin with a lower concentration and apply every other night to build skin tolerance and minimize irritation.
Potential Side Effects
While retinoids offer significant benefits for improving skin texture and reducing the visible signs of aging, they can also come with some side effects, especially when first introduced to your skincare routine. Common reactions include skin irritation, redness, dryness, and flaking, which are more likely to occur in sensitive skin. These effects are usually temporary and can be minimized by starting with a lower concentration and gradually increasing as your skin builds tolerance.
Another possible side effect is skin purging, where dead skin cells and impurities are brought to the surface, sometimes resulting in temporary acne breakouts. This is a normal part of the skin’s adjustment process and typically resolves within a few weeks. To protect your skin and enhance results, always use sunscreen during the day, as retinoids can make your skin more sensitive to sunlight. With patience and proper care, most people find that their skin adapts, allowing them to enjoy the full benefits of retinoids with minimal discomfort.
Prescription Retinoids: How Do They Compare?
Prescription retinoids, such as tretinoin, are considered the gold standard for treating severe acne, uneven skin texture, and advanced signs of aging. These potent formulas work by accelerating cell turnover and boosting collagen production, leading to smoother skin texture and a more youthful appearance. Because prescription retinoids are stronger than over-the-counter options, they can deliver faster and more dramatic results for stubborn skin concerns.
However, this increased potency also means a higher risk of skin irritation, dryness, and peeling, especially for those with sensitive skin or lower skin tolerance. It’s important to consider your skin type and specific needs when choosing between prescription retinoids and milder forms like retinyl esters or over-the-counter retinol. Consulting with a dermatologist can help you determine the best option for your skin, ensuring you achieve healthy, radiant skin while minimizing potential side effects. Whether you’re targeting severe acne, fine lines, or uneven skin texture, the right retinoid can make a world of difference in your skincare journey.
Usage and Application Tips
- Using prescription retinoids correctly is essential to maximize their benefits and minimize side effects. It is generally advised to use retinoids at night to minimize sun sensitivity and start with a lower concentration, gradually increasing usage over time.
- Regular use of retinoids can also help improve the appearance of crepey skin by enhancing skin firmness and elasticity.
- Introducing retinaldehyde slowly into your skincare routine can help mitigate potential side effects.
Application Steps
Beginners should start with lower concentrations of retinaldehyde, such as 0.05%, and apply it twice a week at night to minimize irritation. Due to increased skin sensitivity to sunlight, daily sunscreen use is a must when using retinaldehyde.
Product Pairings
Pairing retinaldehyde with niacinamide can enhance skin radiance and improve texture, making for a powerful combination in your skincare regimen.
Choosing the Right Retinoid for Your Skin Type
Choosing the right retinoid involves considering your skin type and specific concerns. Retinaldehyde typically works better for sensitive skin and offers significant benefits for those with blemish-prone skin. Its higher potency and faster results in reducing signs of aging make it a suitable option for mature skin or those looking for quicker outcomes with anti-aging properties for a youthful appearance, youthful glow, youthful complexion, and skin radiance.

For Acne-Prone Skin
Retinaldehyde is favored for acne-prone skin because of its fast action and effectiveness in treating acne. Its higher potency leads to quicker results, and its unique antibacterial properties help reduce blemishes, making it a more effective choice for managing acne.
For Anti-Aging
Both retinol and retinaldehyde are effective in addressing the signs of aging such as fine lines and uneven texture. Retinol treats fine lines and improves skin texture, while retinaldehyde reduces fine lines and wrinkles more quickly. The faster results make it a preferred choice for those seeking quick anti-aging benefits.
When to Expect Results
Consistency is crucial when using retinoids. The timeline for skin changes and improvements is as follows:
- Initial skin changes can be seen between 2 to 4 weeks after starting a retinoid regimen.
- Visible improvements generally begin within a few weeks of consistent application.
- Significant results may take several months.
Short-Term Effects
Users may notice improvements in skin texture and uneven tone within the first few weeks, with retinaldehyde often showing more rapid results compared to retinol.
Long-Term Benefits
For long-term benefits, at least 6 months of consistent use is typical to see significant improvements from retinoids. After six months, users can expect marked improvements in fine lines, skin firmness, and overall texture. Continued use of retinol and retinaldehyde can lead to notable reductions in the appearance of fine lines and enhancements in skin elasticity.
Summary
In summary, both retinol and retinaldehyde are valuable additions to any skincare routine, offering a range of benefits from improving skin texture to reducing fine lines and treating acne. Retinaldehyde stands out for its potency and quicker results, making it an excellent choice for those looking for rapid improvements. However, retinol remains a reliable option for those new to retinoids or with sensitive skin.
Choosing the right retinoid ultimately depends on your specific skin concerns and how your skin reacts to these powerful ingredients. With consistent use and proper application, you can achieve healthier, more radiant skin. So, why start your journey to better skin today?

Frequently Asked Questions
What are the main differences between retinol and retinaldehyde?
Retinaldehyde is more potent and faster-acting than retinol because it only requires one conversion step to become retinoic acid, while retinol needs two. So if you're looking for quicker results, retinaldehyde might be the better choice!
Which retinoid is better for sensitive skin?
Retinaldehyde is generally considered better for sensitive skin because it causes less irritation and peeling than retinol. If you have sensitive skin, it's a great option to try!
How long does it take to see results from using retinol or retinaldehyde?
You can often notice some initial improvements with retinol or retinaldehyde in about 2 to 4 weeks, but for significant results, you'll need to stick with it for several months. Consistency is key!
Can I use retinoids if I have acne-prone skin?
Absolutely, retinoids like retinol and retinaldehyde are great for acne-prone skin, with retinaldehyde being especially effective due to its potency and antibacterial properties. Just be sure to start slow to avoid irritation!
Should I use retinoids every night?
Use retinoids every other night initially to help your skin adjust and reduce irritation. Once your skin is comfortable, you can gradually increase to nightly use if needed.