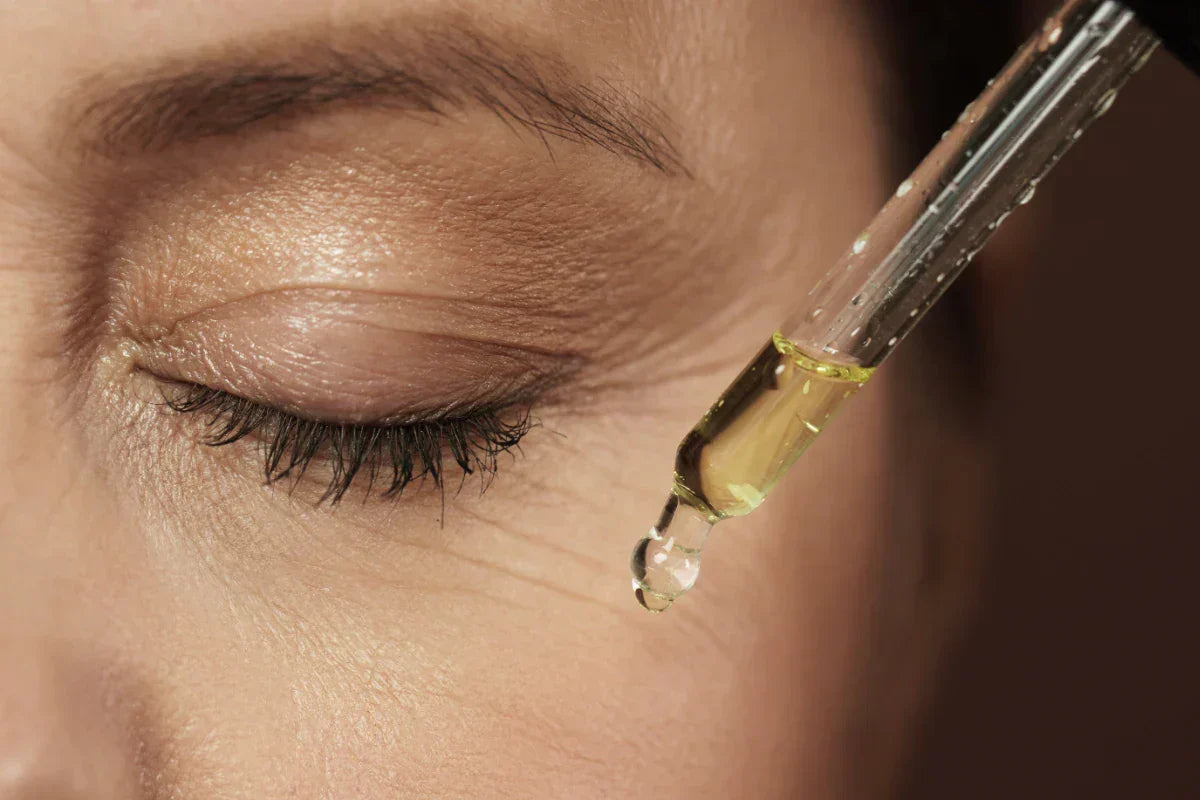
Every day, your skin faces an invisible assault from harmful rays that penetrate clouds, glass, and even indoor lighting. While most people associate sun protection with beach days and summer vacations, the reality is that up to 80% of UV rays can reach your skin regardless of weather conditions, making daily protection essential for preventing premature aging, hyperpigmentation, and serious health concerns.
Understanding how to choose and properly use sunscreen isn’t just about avoiding sunburn; it’s about maintaining healthy, protected skin throughout your lifetime. With countless formulations, SPF ratings, and ingredient combinations available, selecting the right protection can feel overwhelming.
This comprehensive guide will equip you with the knowledge to make informed decisions about sun protection, helping you navigate everything from SPF ratings to application techniques. Whether you’re dealing with oily skin, sensitive skin, or combination skin, this guide provides the essential information you need to create an effective protection routine tailored to your lifestyle and skin type.
What is Sunscreen and Why You Need It
Sunscreen acts as a protective barrier against harmful UV radiation, blue light, and environmental pollutants that constantly threaten skin health. This topical protection works through two primary mechanisms: physically blocking rays or chemically absorbing them before they can penetrate and damage skin cells.
The science behind sun damage reveals why daily protection is non-negotiable. UVB rays primarily affect the outer skin layers, causing the visible redness and pain of sunburn, while UVA rays penetrate deeper into the skin, triggering long-term damage, including hyperpigmentation, premature aging, and DNA mutations that may lead to skin cancer. This exposure stimulates excessive melanin production, contributing to uneven skin tone and stubborn dark spots that become increasingly difficult to treat over time.
Daily sunscreen use prevents both acute and cumulative UV-induced skin damage while controlling inflammation and maintaining a more uniform complexion. The protection remains essential regardless of weather conditions, as research demonstrates that harmful rays can penetrate cloud cover and glass windows. This means your facial skin requires protection whether you’re commuting to work, sitting by a window, or spending time outdoors.

Modern sunscreen formulations also address blue light exposure from electronic devices, which research links to oxidative stress and pigmentary changes. For individuals who spend a significant amount of time in front of computers or smartphones, this additional protection helps prevent the exacerbation of conditions like melasma and supports overall skin health.
Types of Sunscreen Protection
Understanding protection ratings helps you select products that deliver comprehensive defense against various types of harmful radiation. The SPF rating specifically measures protection against UVB rays, with SPF 30 providing approximately 97% protection while SPF 50 blocks about 98% of harmful rays. Although this difference may appear minimal, the additional protection can be significant for individuals with fair skin or those at a higher risk of sun damage.
The PA rating system, commonly used in Asian markets, measures UVA protection levels. Products labeled PA+++ or PA++++ indicate very high defense against the rays responsible for aging and pigmentation changes. This rating system helps consumers understand that effective protection requires defense against both UVA and UVB radiation, not just the SPF rating alone.
Broad-spectrum protection represents the gold standard in sunscreen formulations, as products must demonstrate efficacy against both UVA and UVB rays to earn this designation. Regulatory authorities, such as the FDA, mandate this comprehensive protection to ensure that consumers receive adequate photoprotection from a single product.
Blue light protection has become an increasingly important consideration for modern lifestyles. Ingredients such as iron oxides and antioxidants, including vitamin C and niacinamide, are increasingly added to formulations to protect against visible light-induced pigmentation. This protection is particularly valuable for individuals who spend extended periods exposed to electronic screens, as studies have linked prolonged blue light exposure to oxidative stress and the worsening of certain pigmentation conditions.
The highest SPF products available typically range from SPF 50 to SPF 100. However, dermatologists generally recommend SPF 30-50 for daily use, as proper application and reapplication are more important than extremely high SPF numbers. For those seeking maximum sun protection, choosing a sunscreen labeled as SPF 50 PA+++ or SPF 50 PA++++ ensures broad-spectrum coverage against both UVA and UVB rays, making it ideal for individuals who require high protection levels.
Sunscreen Formulations and Ingredients
The choice between mineral and chemical sunscreen formulations depends on skin sensitivity, lifestyle needs, and personal preferences. Each type offers distinct advantages and works through different mechanisms to provide protection. Mineral sunscreens use zinc oxide and titanium dioxide to physically reflect UV rays away from the skin, creating an immediate barrier upon application.
These ingredients are particularly suitable for sensitive skin types, as they’re less likely to cause irritation and are generally recognized as safe by health authorities. Modern formulations have largely eliminated the white cast issue through the use of micronized particles that blend seamlessly into most skin tones. Chemical sunscreens rely on organic compounds such as avobenzone, octinoxate, and oxybenzone to absorb UV energy and convert it into heat, which dissipates from the skin.
While these formulations often provide more cosmetically elegant, lightweight textures, some ingredients have raised safety concerns due to potential skin penetration and environmental impact. Gel formulations offer lightweight, non-greasy application that’s particularly ideal for oily and combination skin types. These water-based formulas absorb quickly without leaving sticky residue, making them excellent for daily use under makeup or for those who prefer minimal texture on their skin.
Enhanced formulations are powered by advanced ingredients or technologies that provide additional benefits beyond sun protection. Hyaluronic acid and ceramides maintain skin hydration throughout sun exposure, while antioxidants like vitamin C help combat oxidative stress from environmental pollutants.
Key Active Ingredients
Pure zinc oxide at concentrations up to 25% creates an effective invisible barrier without the traditional white cast associated with older formulations. This ingredient provides robust, broad-spectrum protection while remaining gentle enough for daily use on all skin types, including acne-prone skin.
Titanium dioxide provides mild, hypoallergenic protection, particularly favored for sensitive skin and infant formulations. This mineral ingredient offers reliable protection against UVB and shorter UVA rays with minimal risk of irritation, making it suitable for individuals who experience reactions to chemical filters.
Moisturizing ingredients, such as glycerin and hyaluronic acid, help maintain proper hydration levels during prolonged sun exposure. These humectants draw moisture from the environment and deeper skin layers, preventing the dryness that can occur with prolonged outdoor activities or in air-conditioned environments.
Natural extracts, including raspberry seed oil and shea butter, provide additional nourishment while supporting the skin’s protective barrier. These botanical ingredients offer antioxidant benefits and help soothe stressed skin resulting from environmental exposure, creating a more comprehensive approach to skin health.
Choosing Sunscreen for Different Skin Types
Selecting the appropriate sunscreen formulation requires understanding your specific skin needs and how different ingredients interact with various skin types. The right choice can make the difference between consistent daily use and a product that sits unused in your medicine cabinet.
Oily skin benefits from non-comedogenic, lightweight gel or fluid formulations that won’t clog pores or contribute to excess shine. Look for products labeled as suitable for acne-prone skin, as these formulations are specifically designed to provide protection without triggering breakouts. Water-based formulas with a non-sticky formulation work particularly well for this skin type, as they absorb quickly and don’t leave an oily texture that can feel uncomfortable throughout the day.

Sensitive skin requires gentle, mineral-based formulations with minimal additional ingredients that could trigger reactions. Hypoallergenic products, free from fragrances, preservatives, and common allergens, provide the safest option for sensitive skin. It’s advisable to perform a patch test before using any new product extensively, applying a small amount to the inner wrist and waiting 24-48 hours to check for any adverse reactions.
Dry skin requires hydrating formulas that incorporate moisturizing ingredients, such as ceramides, glycerin, and hyaluronic acid. These formulations serve dual purposes, providing essential protection while addressing the skin’s moisture needs. Look for cream-based products that offer a more emollient texture, helping to maintain the skin’s barrier function while delivering comprehensive sun protection.
Combination skin requires balanced formulations that protect without causing excess oil in the T-zone or dryness in other areas. Products that blend easily and don’t leave residue work well for this skin type, as they can adapt to the needs of different areas without creating an uneven appearance or an uncomfortable texture.
Consider your daily activities when making selections. Those who spend time swimming or sweating extensively need sweat-resistant formulations. At the same time, individuals who wear makeup daily might prefer products that work well as primers and don’t interfere with cosmetic application.
Selecting the Right Sunscreen for Your Needs
Choosing the best sunscreen for your skin type and lifestyle can be overwhelming with the numerous brands, formulations, and features available on the market. To simplify the process, start by identifying your primary skin concerns, such as oily, sensitive, combination, or dry skin, and consider how your daily activities impact your sun exposure.
For oily or acne-prone skin, opt for lightweight, non-greasy, and non-comedogenic formulations such as gels or fluids. These products absorb quickly, won’t clog pores, and help control shine throughout the day. If you have sensitive skin, look for mineral-based sunscreens that contain zinc oxide or titanium dioxide, as these ingredients are less likely to cause irritation and are suitable for even the most sensitive complexions.
Combination skin benefits from balanced formulas that hydrate dry areas without adding excess oil to the T-zone. Cream-gel hybrids or water-based lotions often offer the ideal balance of moisture and protection. For individuals with dry skin, look for hydrating sunscreens enriched with hyaluronic acid, ceramides, or glycerin to help maintain moisture and support the skin barrier during sun exposure.
Consider your environment and routine: If you spend long hours in front of screens, a sunscreen with blue light protection and antioxidants like vitamin C can help defend against digital pollution. For outdoor enthusiasts or those who sweat or swim, sweat-resistant and water-resistant options are essential for maintaining efficacy.
Don’t forget to check the SPF rating and look for broad-spectrum protection to shield against both UVA and UVB rays. Tinted sunscreen is a great choice for those who want to even out their complexion while protecting against visible light. Invisible or non-sticky formulations are ideal for layering under makeup or for those who dislike residue.
Always read the label for features that match your needs, whether it’s a dewy finish, non-greasy feel, or added skincare benefits. Performing a patch test is advisable when trying a new product, especially for sensitive or combination skin types. By aligning your sunscreen choice with your unique skin type, daily habits, and personal preferences, you’ll be more likely to use it consistently and enjoy the full benefits of sun protection.
Sunscreen for Active Lifestyles
If your days are filled with outdoor adventures, workouts, or frequent swimming, your sunscreen needs to keep up with your active lifestyle. The best sunscreen for active individuals is one that offers sweat-resistant and water-resistant protection, ensuring your skin stays shielded from harmful UV rays even during intense activity or exposure to water.
Look for formulations specifically labeled as “sport” or “active,” as these are designed to adhere better to the skin and maintain their SPF rating through sweating and swimming. Stick and spray formats are especially convenient for quick, mess-free reapplication on exposed areas like the face, neck, ears, and shoulders, which are often overlooked but highly susceptible to sun damage.

Non-sticky and non-greasy textures are a must for those who dislike the feeling of heavy residue during exercise. Lightweight gels and fluid sunscreens blend easily, won’t clog pores, and are less likely to cause irritation or breakouts, making them suitable for oily skin and combination skin types.
Remember, even the highest SPF and most sweat-resistant formulas require regular reapplication, ideally, every two hours and immediately after swimming, sweating, or towel drying. Carry a travel-sized bottle or stick in your gym bag or backpack so you’re always prepared to reapply, no matter where your day takes you.
For those who spend extended periods outdoors, consider layering your sun protection with UPF-rated clothing, hats, and sunglasses for comprehensive defense. By choosing the right sunscreen features and making reapplication a habit, you can enjoy your active lifestyle while keeping your skin healthy, protected, and glowing.
Proper Sunscreen Application and Reapplication
Effective protection depends not only on choosing the right product but also on applying adequate amounts at appropriate intervals. Most people use significantly less sunscreen than needed, which dramatically reduces the actual protection received, regardless of the SPF rating on the bottle.
The proper quantity for facial protection requires approximately two finger-lengths of product, which translates to about 1/4 teaspoon for the face and neck combined. This amount ensures you receive the protection level indicated on the product label. Apply sunscreen as the final step in your skincare routine, after moisturizer but before makeup, allowing 15-20 minutes for absorption before sun exposure.
Timing matters significantly for optimal efficacy. Apply sunscreen 20 minutes before anticipated sun exposure to allow the ingredients to form a protective barrier on the skin. This is particularly important for chemical formulations, which need time to bind with the skin and begin working effectively.
Reapplication every two hours represents the minimum frequency for maintaining protection, though this schedule increases to immediately after swimming, sweating, or toweling off. Even water-resistant formulations require reapplication, as no product is truly waterproof. The FDA requires water resistance testing at either 40 or 80-minute intervals, but these timeframes assume ideal conditions and normal activity levels.
Don’t neglect commonly missed areas that are particularly susceptible to damage. The ears, lips, scalp (especially along hair parts), backs of hands, and tops of feet are frequently exposed parts of the body that receive inadequate protection. These areas often show the first signs of sun damage and require the same careful attention as facial skin.
For those who wear makeup, consider using powder sunscreens or spray formulations for midday touch-ups, although these should supplement, rather than replace, proper morning application. Tinted sunscreen can serve double duty, providing light coverage while offering protection, making reapplication throughout the day more convenient.
Common Sunscreen Mistakes to Avoid
Even the most diligent sunscreen users can fall into common traps that compromise their sun protection. Avoiding these mistakes is key to ensuring your skin receives the full benefits of your chosen product. One of the most frequent errors is applying too little sunscreen. For effective coverage, use approximately a quarter teaspoon for your face and neck, and don’t forget other exposed areas, such as the ears, the back of your hands, and the tops of your feet.
Skipping these areas leaves your skin vulnerable to sun damage and uneven skin tone. Another mistake is neglecting to reapply sunscreen throughout the day. No matter how high the SPF rating or how sweat-resistant the formulation, all sunscreens lose efficacy over time, especially when exposed to sweating, swimming, or towel drying. Set reminders to reapply every two hours, and more often during intense sun exposure or physical activity.
Relying solely on makeup or moisturizers with SPF can also lead to inadequate protection. These products often don’t provide enough coverage or broad-spectrum protection on their own. Always use a dedicated sunscreen as the final step in your skincare routine, and layer additional products as needed.

Using expired sunscreen is another pitfall. Over time, active ingredients degrade, reducing the product’s efficacy. Check expiration dates and replace your sunscreen every 2-3 years, or sooner if it’s been exposed to heat or direct sunlight.
Finally, don’t assume that darker skin tones are immune to sun damage. All skin types are susceptible to the harmful effects of UV rays, including premature aging and increased risk of skin cancer. Consistent, proper application is essential for everyone, regardless of complexion. By steering clear of these common mistakes and following best practices, you’ll maximize your sunscreen’s protective power and support your skin’s long-term health.
Special Features and Benefits
Modern sunscreen innovations cater to specific lifestyle needs and preferences, offering features that enhance both protection and the user experience. Understanding these options helps you select products that fit seamlessly into your daily routine.
Water-resistant formulations maintain their stated SPF protection for either 40 or 80 minutes during swimming or sweating, as verified through FDA-mandated testing. These products utilize specialized binding agents that help the sunscreen adhere to the skin, even when it is wet. However, they still require reapplication after the designated time period or after toweling off.
Tinted sunscreen provides light coverage while protecting against both UV and blue light exposure. The iron oxides that create the tint also enhance protection against visible light, making these products particularly suitable as makeup primers for everyday use. The range of available shades has expanded significantly, accommodating diverse skin tones and eliminating the need for separate foundation products during casual activities.
Invisible formulas eliminate the white cast and residue that historically made people reluctant to use adequate amounts of sunscreen. These advanced formulations blend seamlessly into all skin tones, encouraging more consistent use and proper application quantities. The improved aesthetics make daily protection more appealing, particularly for those who previously avoided sunscreen due to cosmetic concerns.
Stick formats offer a convenient on-the-go application for active lifestyles and targeted protection of specific areas. These solid formulations work particularly well for lip protection, around the eyes, and for reapplication during outdoor activities. The portability makes it easier to maintain protection throughout the day, especially for areas that receive frequent exposure.
Antioxidant-enhanced formulations offer an additional defense against environmental stressors, including those beyond UV radiation. Ingredients such as vitamin C, niacinamide, and green tea extract help neutralize free radicals from pollution and other environmental factors, creating a more comprehensive approach to skin protection and overall health.
Sunscreen and Skin Health
Sunscreen is more than just a shield against sunburn it’s a cornerstone of overall skin health. Consistent use helps prevent the development of uneven skin tone, dark spots, and premature signs of aging, such as fine lines and dullness. By blocking both UVA and UVB rays, broad-spectrum protection preserves your skin’s natural glow and supports a dewy, hydrated complexion.
Modern sunscreens often include skin-loving ingredients like hyaluronic acid, ceramides, and antioxidants, which work together to maintain moisture, strengthen the skin barrier, and combat environmental stressors like pollution and blue light. This synergy not only protects against immediate sun damage but also reduces irritation and supports the skin’s ability to repair itself.
For those with sensitive or acne-prone skin, choosing the right formulation can help minimize flare-ups and maintain a calm, balanced complexion. Mineral sunscreens with zinc oxide or titanium dioxide are gentle enough for daily use and can even soothe irritated skin.
Regular sunscreen use is also a proactive step in reducing the risk of skin cancer and other serious health concerns. By making sun protection a daily habit, you’re investing in the long-term health and resilience of your skin, ensuring it remains vibrant and youthful for years to come.
Sunscreen and Daily Life
Incorporating sunscreen into your everyday routine is one of the simplest yet most effective ways to protect your skin from the cumulative effects of sun exposure. Whether you’re heading to the office, running errands, or spending time indoors near windows or screens, daily application is essential for maintaining healthy, radiant skin. Select a sunscreen with a lightweight, non-greasy formulation that blends seamlessly into your morning skincare routine.
Apply it as the final step before makeup, and allow a few minutes for it to absorb fully. For those who wear makeup, opt for invisible or tinted sunscreen options that double as a primer, ensuring even coverage without a white cast or residue. Keep a travel-sized bottle or stick in your bag for easy reapplication throughout the day, especially if you’re commuting, spending time outdoors, or exposed to bright indoor lighting.
Setting a daily reminder or pairing sunscreen application with another habit, such as brushing your teeth, can help make sun protection second nature. If you have oily or combination skin, look for products that control shine and won’t clog pores, allowing you to reapply as needed with confidence. For dry skin, hydrating formulas with added moisture will keep your complexion looking fresh and dewy all day.
Remember, sun protection isn’t just for summer or sunny days. UV rays and blue light can affect your skin year-round, indoors and out. By making sunscreen a non-negotiable part of your daily life, you’re taking a powerful step toward preserving your skin’s health, beauty, and youthful glow no matter where your day takes you.
Common Sunscreen Myths and Facts
Despite widespread awareness of the importance of sun protection, persistent misconceptions continue to influence people’s sunscreen habits and choices. Addressing these myths helps ensure more effective protection strategies.
The belief that sunscreen is unnecessary on cloudy days represents one of the most dangerous misconceptions. Research indicates that up to 80% of UV rays can penetrate cloud cover, suggesting that overcast conditions offer minimal natural protection. UVA rays, which cause the majority of long-term skin damage, maintain consistent intensity throughout the day regardless of visible sunshine, making daily protection essential.

Indoor workers are increasingly in need of protection from blue light exposure from screens and electronic devices. While traditional sun protection focused primarily on outdoor activities, modern lifestyles involve extensive screen time that contributes to oxidative stress and can exacerbate certain pigmentation conditions. Sunscreen with blue light protection ingredients provides valuable defense for individuals who spend a significant amount of time indoors using electronic devices.
The assumption that darker skin tones don’t require sun protection overlooks important health realities. While higher natural melanin levels provide some inherent protection, all skin types remain susceptible to cumulative UV damage and hyperpigmentation. Skin cancer, though less common in darker skin tones, often goes undetected longer and may be more aggressive when it occurs, making protection equally important for everyone.
No sunscreen is truly waterproof; only water-resistant options exist, and all require regular reapplication. The terms “waterproof” and “sweatproof” are no longer permitted in sunscreen marketing because they create false expectations about the duration of protection. Even the most advanced water-resistant formulations lose their effectiveness over time and with continued use, necessitating consistent reapplication for sustained protection.
The misconception that higher SPF provides proportionally better protection leads to inadequate application and false confidence. While SPF 50 does provide marginally better protection than SPF 30, the difference is minimal (98% vs 97%), and proper application technique matters far more than SPF numbers above 30.
Maximizing Your Sun Protection Routine
Comprehensive sun protection extends beyond sunscreen application to include multiple defensive strategies that work synergistically to minimize damage and maintain skin health throughout your lifetime. Combine sunscreen with protective clothing, wide-brimmed hats, and sunglasses for enhanced defense during outdoor activities. Physical barriers provide reliable protection that doesn’t require reapplication and can be particularly valuable during periods of peak exposure.
Look for clothing with UPF ratings for quantified protection levels, especially when engaging in extended outdoor activities. Seek shade during peak sun hours between 10 AM and 4 PM when solar radiation reaches its highest intensity. This simple strategy significantly reduces overall exposure while allowing you to enjoy outdoor activities with less risk. Even brief periods in shade can provide meaningful protection during high-intensity exposure periods.
Monitor expiration dates and replace sunscreen every 2-3 years for optimal efficacy, as active ingredients can degrade over time, especially when exposed to heat or light. Products stored in hot cars or direct sunlight may lose effectiveness even before their expiration dates. Consider the storage conditions and purchase smaller quantities if you don’t use sunscreen frequently to ensure freshness.
Consider your daily activities when choosing between regular and sport formulations. Those who exercise outdoors, swim regularly, or work in high-exposure environments benefit from sport formulations designed for extended wear and sweat-resistant properties. Office workers might prioritize elegant formulations that work well under makeup and provide blue light protection.
Layer protection by using sunscreen in combination with antioxidant serums, moisturizers with SPF, and makeup products containing sun protection ingredients. This comprehensive approach provides multiple layers of defense, helping to ensure adequate coverage even if one layer wears off during the day.
Regular skin examinations and professional dermatological checkups complement daily protection habits by identifying any changes or concerns early. Prevention through consistent sunscreen use, combined with professional monitoring, creates the most effective strategy for maintaining long-term skin health and detecting potential problems before they become serious.
The power of consistent daily sunscreen application extends far beyond preventing immediate sunburn to encompass long-term skin health, appearance, and protection against serious conditions. By understanding the science behind sun protection, selecting suitable formulations for your skin type, and applying products correctly, you establish a foundation for healthy skin that will benefit you throughout your lifetime.
Building an effective sun protection routine requires combining quality products with proper technique and realistic expectations about reapplication needs. Whether you’re protecting oily skin, sensitive skin, or combination skin, the right approach to sunscreen use can help you maintain a healthy, protected complexion while supporting your overall skin health goals.
Start building your comprehensive sun protection routine today by selecting a broad-spectrum sunscreen appropriate for your skin type and committing to daily application, regardless of weather conditions or indoor activities.
Frequently Asked Questions on Sunscreens
Why should I wear sunscreen every day, even indoors or on cloudy days?
Up to 80% of UV rays can penetrate clouds and windows, making daily sunscreen essential, even on cloudy days or when indoors. Sunscreen protects your skin from premature aging, hyperpigmentation, and long-term damage, such as skin cancer.
What does SPF mean, and how much should I use?
SPF (Sun Protection Factor) measures protection against UVB rays. SPF 30 blocks about 97% and SPF 50 blocks about 98% of UVB radiation. Use about 1/4 teaspoon for your face and reapply every 2 hours for full coverage.
What is the difference between mineral and chemical sunscreen?
Mineral sunscreens, which use zinc oxide or titanium dioxide to reflect UV rays, are ideal for individuals with sensitive skin. Chemical sunscreens absorb UV rays and offer lightweight textures. Choose based on your skin type and comfort.
Which sunscreen is best for oily or acne-prone skin?
Gel-based or water-based sunscreens are best for oily or acne-prone skin. Look for “non-comedogenic” and “oil-free” formulas that absorb quickly without clogging pores or causing shine.
How often should I reapply sunscreen during the day?
Reapply sunscreen every 2 hours, and immediately after swimming, sweating, or towel drying. Even water-resistant sunscreens lose effectiveness over time and need frequent reapplication for complete protection.
Can sunscreen protect against blue light from screens?
Yes. Some sunscreens contain ingredients such as iron oxides, niacinamide, and vitamin C that help protect against blue light emitted by phones and computers, which can lead to pigmentation and oxidative stress.
Is sunscreen necessary for darker skin tones?
Yes. Darker skin can still suffer from sun damage, hyperpigmentation, and skin cancer. Daily sunscreen use helps protect and maintain a healthy, even complexion for all skin tones.
What should I look for in a daily sunscreen?
Choose a broad-spectrum sunscreen with SPF 30 or higher, suitable for your skin type. Look for added benefits, such as hydration, blue light protection, or tinted formulas, if desired. Make sure it feels comfortable so you’ll use it daily.