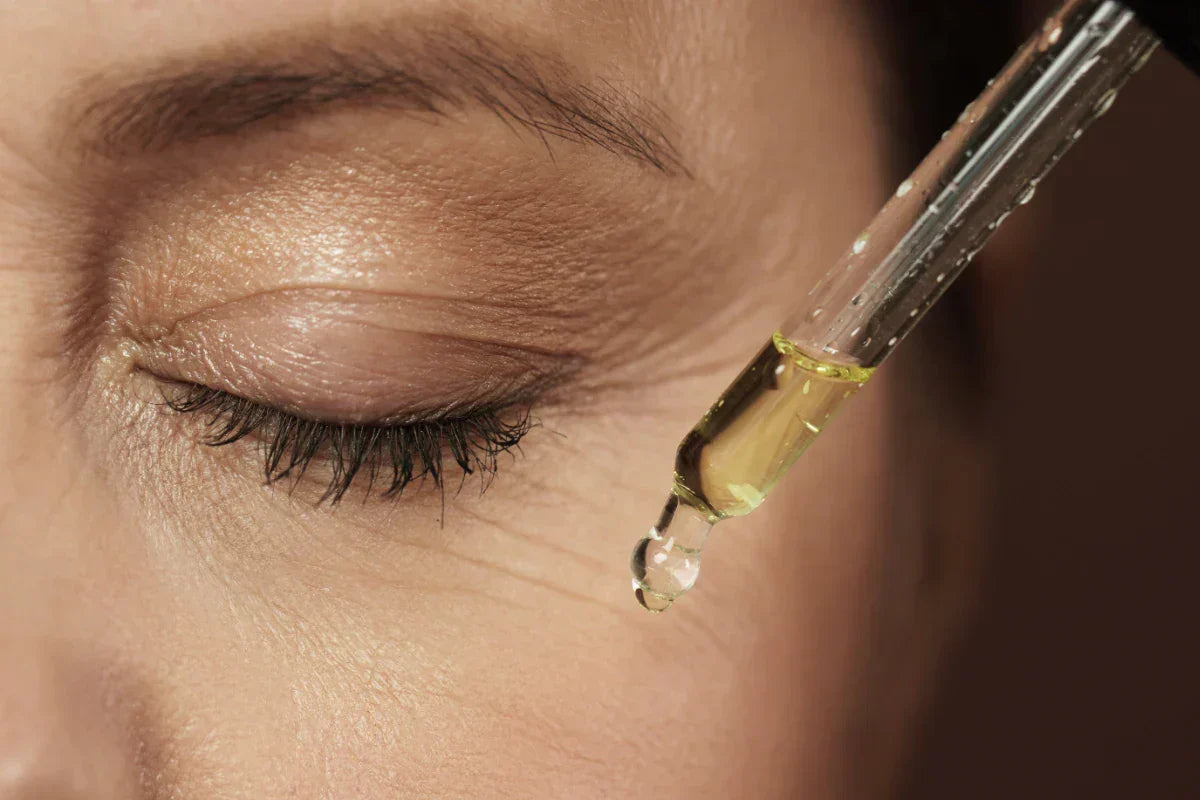
Deep within the tropical papaya fruit lies papain, a powerful proteolytic enzyme derived from Carica papaya, that has become a key ingredient in the cosmetics industry. Papain is an enzyme found naturally in papaya, especially in the latex of the unripe fruit. It is also known as papaya proteinase or papaya proteinase I. Papain is commonly extracted from papaya latex for use in cosmetics. Known for its protein-breaking properties and anti-inflammatory effects, papain is widely used in skincare formulations to promote healthy, radiant skin.
Its versatility extends from gentle exfoliation to wound healing support, making it a valuable natural component in beauty and personal care products. This guide focuses specifically on the role of papain in cosmetics, exploring its benefits for skin health, applications in various products, safety considerations, and emerging research that highlights its potential in modern skincare. Papaya extracts, rich in papain, are often used in cosmetic formulations for their enzymatic and skin benefits.
What is Papain?
Papain is a proteolytic enzyme naturally found in the papaya tree, scientifically known as Carica papaya. As a cysteine protease belonging to the papain family of enzymes, papain functions by breaking down proteins through proteolytic cleavage, targeting peptide bonds between amino acids. Papain is part of a broader family of cysteine proteinases, which share similar structural and functional features. Papain and related enzymes are classified as cysteine peptidases due to their catalytic mechanism involving a cysteine residue in the active site.
Papain is a prototypical member of the papain like cysteine proteinases, which are widely studied for their enzymatic activity. This enzymatic activity enables papain to gently remove dead skin cells and promote tissue renewal, making it an effective ingredient in cosmetic products. The enzyme is most concentrated in the latex of unripe papaya fruit, where papain activity is highest. Crude papaya latex contains papain along with other enzymes, which are later purified for cosmetic use.
Commercially, papain extract is available in purified forms suitable for cosmetic use, often incorporated into creams, lotions, exfoliants, and specialized treatments for skin lesions and inflammatory skin diseases. Papain is used in a variety of industries, including cosmetics, food processing, and pharmaceuticals, due to its versatile enzymatic properties.

History and Overview of Papain
Papain, a renowned proteolytic enzyme, has its roots in the latex of the unripe fruit of the Carica papaya tree. As a member of the cysteine protease family, often referred to as the papain family, this enzyme is distinguished by its ability to break down complex proteins into smaller peptides and amino acids through proteolytic cleavage. The structure of papain, composed of 212 amino acids and stabilized by four disulfide bridges, underpins its robust enzymatic activity and versatility across various applications.
Historically, papain was valued in traditional medicine as a natural remedy for treating wounds, reducing tissue swelling, and managing skin diseases. Its use dates back centuries, with indigenous cultures harnessing the enzyme’s properties to support wound healing and relieve pain. The scientific isolation of papain from the papaya tree in the early 19th century marked a turning point, paving the way for its adoption in the food, pharmaceutical, and cosmetic industries.
In the food industry, papain is widely recognized as a meat tenderizer, thanks to its efficient proteolytic activity. The enzyme’s ability to break down tough muscle fibers has made it a staple in culinary preparations. In the pharmaceutical sector, purified papain is available in powder form and as papain supplements, often marketed for their potential to improve digestion and alleviate digestive disorders. Limited research suggests that papain may also offer anti-inflammatory properties, making it a candidate for managing inflammatory diseases and metabolic syndrome, although more research is needed to confirm these health benefits.
Papain’s mechanism of action is closely tied to its active site and catalytic triad, which enable precise proteolytic cleavage. This enzymatic function is not only beneficial for digestion but also for topical applications, such as papain salves and creams used to support wound healing and treat skin lesions. Throat lozenges containing papain have been used to soothe sore throat symptoms, though their effectiveness remains under investigation.
Despite its many beneficial effects, papain is not without risks. Some individuals may experience serious allergic reactions, including throat irritation and low blood pressure, particularly those with sensitivities to latex or certain fruits. The Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has classified papain as generally recognized as safe (GRAS) for use as a food additive, but cautions remain regarding its use in topical and supplemental forms.

Consulting a healthcare provider before using products containing papain is strongly recommended, especially for those with pre-existing allergies or health conditions. Some experiments have also shown that papain may help reduce weight gain and improve markers of metabolic syndrome, but these findings are preliminary. As with many natural remedies, more research is necessary to fully understand the scope of papain’s health benefits and its impact on the immune system and inflammatory response.
In summary, papain is a multifaceted enzyme with a rich history and a broad spectrum of uses. From its origins in the papaya tree to its modern applications in food, pharmaceuticals, and cosmetics, papain continues to attract interest for its proteolytic and anti-inflammatory properties. While it holds promise as a natural remedy for various conditions, responsible use and further scientific investigation are essential to ensure its safety and efficacy.
Cysteine Protease Biochemical Properties Relevant to Cosmetics
Papain’s unique three-dimensional structure and catalytic triad, particularly the cysteine-25 and histidine-159 residues, underpin its ability to selectively break down proteins. In cosmetics, this translates to efficient exfoliation by dissolving keratin and other protein components of dead skin cells without damaging underlying healthy tissue.
Its proteolytic action also contributes to anti-inflammatory effects, helping to soothe irritated skin and support the healing of minor wounds or lesions. Papain’s enzymatic stability across a broad pH range and temperature spectrum ensures its effectiveness in various cosmetic formulations.
Cosmetic Benefits of Papain
Gentle Exfoliation and Skin Renewal
Papain is prized in skincare for its ability to exfoliate gently yet effectively. By breaking down the protein bonds in dead skin cells, papain promotes their removal, revealing fresher, smoother skin beneath. This enzymatic exfoliation can improve skin texture, reduce dullness, and enhance the absorption of other active ingredients. Unlike harsh physical scrubs, papain minimizes irritation and inflammation, making it suitable for sensitive skin types and conditions prone to redness or sensitivity.
Anti-Inflammatory Effects
Papain exhibits anti-inflammatory properties that help calm skin inflammation associated with conditions such as acne, eczema, and psoriasis. By modulating inflammatory markers and reducing swelling, papain-containing products can soothe irritated skin, reduce inflammation, and support skin barrier repair. These properties also make papain beneficial in post-procedure skincare, aiding recovery after treatments like chemical peels or microdermabrasion.
Wound Healing and Skin Lesion Treatment
In clinical cosmetic applications, papain is utilized for its debriding capabilities, removing dead or damaged tissue to promote healing. Papain is commonly used in wound treatment to promote healing and manage chronic skin lesions. This makes it valuable in managing chronic skin lesions, scars, and minor wounds. Papain’s selective proteolytic action supports tissue regeneration and reduces the risk of infection by clearing cellular debris, contributing to improved skin appearance and health.

Anti-Aging and Skin Brightening
By enhancing cell turnover and removing protein buildup, papain can contribute to reducing the appearance of fine lines, wrinkles, and hyperpigmentation. Its exfoliating effect promotes a more even skin tone and a radiant complexion. Papain-based products may also be beneficial for certain skin conditions that affect skin tone and texture. Papain’s antioxidant properties also help protect skin cells from oxidative stress, a key factor in premature aging.
Cosmetic Applications and Products
Papain is incorporated into a variety of cosmetic products, including:
- Enzyme-based exfoliating masks and peels
- Anti-aging creams and serums
- Acne treatment formulations
- Scar and wound care ointments
- Gentle facial cleansers and body lotions
Its versatility allows formulators to create products targeting diverse skin concerns while leveraging papain’s natural origin and multifunctional benefits.
Safety and Regulatory Considerations
While papain offers many cosmetic benefits, safety is paramount. The Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has issued warnings regarding unapproved topical papain products due to reports of serious allergic reactions, including anaphylaxis and skin irritation. Individuals should be cautious when they consume papain, whether through supplements or natural sources like ripe papayas, due to potential health risks.
Consumers with allergies to latex, kiwi, or figs should exercise caution, as cross-reactivity may occur. Patch testing before use is recommended to minimize adverse reactions. Oral administration of papain, such as in supplement form, should only be done under medical supervision to avoid adverse effects. Cosmetic products containing papain should be used according to the manufacturer's instructions, and professional guidance is advised for treatments involving higher concentrations or clinical applications.

Future Directions in Papain Cosmetic Research
Ongoing research aims to optimize papain’s stability and efficacy in cosmetic formulations, explore recombinant production methods for consistent quality, and investigate synergistic effects with other natural ingredients. Pharmaceutical industries are actively exploring new applications and formulations of papain for both cosmetic and therapeutic purposes. Advancements in delivery systems may enhance papain’s skin penetration and targeted action, expanding its role in personalized skincare.
Conclusion
Papain, the proteolytic enzyme from the papaya tree, is a powerful and versatile ingredient in cosmetics. Its gentle exfoliation, anti-inflammatory, wound healing, and anti-aging properties make it a valuable natural component for promoting healthy, radiant skin. Choosing reliable papain suppliers ensures you receive high-quality enzyme extracts suitable for safe and effective cosmetic formulations.
With appropriate use and safety considerations, papain-containing cosmetic products can offer effective solutions for a range of skin concerns, aligning with the growing demand for natural and scientifically supported skincare ingredients. For those interested in incorporating papain into their skincare routine, choosing reputable products and consulting with skincare professionals ensures the best outcomes and minimizes risks.
Frequently Asked Questions on Papain in Cosmetics (FAQ)
1. What is papain in skincare?
Papain is a natural proteolytic enzyme from the papaya fruit used in skincare for gentle exfoliation, brightening, and improving skin texture.
2. How does papain benefit the skin?
Papain helps remove dead skin cells, reduces dullness, calms inflammation, supports wound healing, and promotes smoother, radiant skin.

3. Is papain safe for all skin types?
Papain is generally safe for most skin types, but people with latex or fruit allergies (like kiwi or fig) should use it cautiously. A patch test is recommended.
4. Which cosmetic products contain papain?
Papain is commonly found in enzyme exfoliators, face masks, cleansers, anti-aging creams, acne treatments, and scar-care formulations.
5. Can papain help with acne or dark spots?
Yes. Papain gently unclogs pores, reduces inflammation, boosts skin renewal, and helps fade dark spots for a clearer, more even complexion.