The world of topical retinoids can feel overwhelming, with countless options promising anti-aging effects while threatening skin irritation and sensitivity. Retinol and its derivatives are available in many forms, such as creams, serums, and other cosmetic products, making these ingredients widely accessible in skincare routines. If you’ve struggled with harsh prescription retinoid formulations or found retinol too slow to deliver results, there’s a compelling middle ground that deserves your attention: Retinaldehyde.
This bioactive form of vitamin A sits perfectly between gentle retinol and potent tretinoin, offering faster visible results without the severe side effects that often accompany stronger retinoids. Unlike many skincare ingredients that rely on marketing hype, retinaldehyde has robust clinical research supporting its effectiveness for reducing fine lines and wrinkles, treating acne, and improving overall skin texture.
In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore everything you need to know about retinaldehyde, from its unique molecular biology to practical application tips that will help you achieve your best skin yet.
What is Retinaldehyde?
Retinaldehyde, also known simply as retinal, represents a fascinating intersection of pure and applied chemistry in skincare. This vitamin A derivative belongs to the retinoid family but occupies a unique position in the conversion pathway, making it particularly effective for topical treatment.
Discovered in the 1980s, retinaldehyde initially gained recognition in visual biochemistry before researchers realized its potential for skincare applications. The molecule appears as yellow or orange crystals with a melting point between 61-64°C, and its chemical formula C₂₀H₂₈O reflects its aldehyde structure.
What sets retinaldehyde apart from other retinoids is its position in the natural vitamin A conversion pathway. While the skin naturally converts retinol to retinaldehyde and then to retinoic acid, retinaldehyde bypasses one conversion step entirely. This proximity to the final bioactive form gives it approximately 10 times greater vitamin A activity than retinol, making it significantly more potent while remaining gentler than prescription options.
The first retinoid many people encounter is typically retinol, found in countless over-the-counter products. However, retinaldehyde’s unique molecular basis allows it to deliver faster results without the irritating side effects that often discourage people from maintaining a consistent skincare routine.
How Retinaldehyde Works in the Skin
Understanding how retinaldehyde functions requires examining the intricate molecular biology of vitamin A metabolism in skin cells. When you apply retinaldehyde to your skin surface, it penetrates the epidermis and undergoes a single oxidation step via retinaldehyde dehydrogenases to become retinoic acid.
This conversion process is remarkably efficient compared to other retinoids. While retinol must undergo two enzymatic conversions and retinyl esters require three steps, retinaldehyde needs only one transformation to become fully bioactive. This efficiency translates to faster visible improvements in skin condition.
Once converted to retinoic acid, retinaldehyde binds to nuclear retinoid receptors, specifically RAR (Retinoic Acid Receptors) and RXR (Retinoid X Receptors). This binding triggers gene expression changes that regulate several crucial skin processes:
- Cell turnover acceleration: Enhanced keratinocyte proliferation removes dead skin cells more efficiently, revealing fresher skin underneath
- Collagen synthesis stimulation: Activated fibroblasts produce more collagen while matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs) are inhibited, reducing collagen loss
- Improved barrier function: Enhanced epidermal renewal strengthens the skin barrier, reducing transepidermal water loss
The immune system also benefits from retinaldehyde’s anti-inflammatory properties, which help calm irritation and reduce redness associated with various skin conditions.
Benefits of Retinaldehyde for Skin
Clinical research has documented impressive benefits from retinaldehyde use, with studies showing measurable improvements within just a few months of consistent application. Here’s what you can expect when incorporating this powerful ingredient into your skincare routine.
Anti-Aging and Wrinkle Reduction
The most compelling evidence for retinaldehyde comes from its ability to reduce fine lines and wrinkles. Research using 0.05% retinaldehyde formulations demonstrates significant improvements in skin texture and firmness within 12 weeks. The mechanism involves both increased collagen production and protection of existing collagen from degradation.
Unlike treatments that only address the skin surface, retinaldehyde works at the cellular level to rebuild the dermal matrix. This comprehensive approach means improvements continue to develop over time, with six-month studies showing increased epidermal thickness and enhanced skin elasticity.
Acne Treatment and Prevention
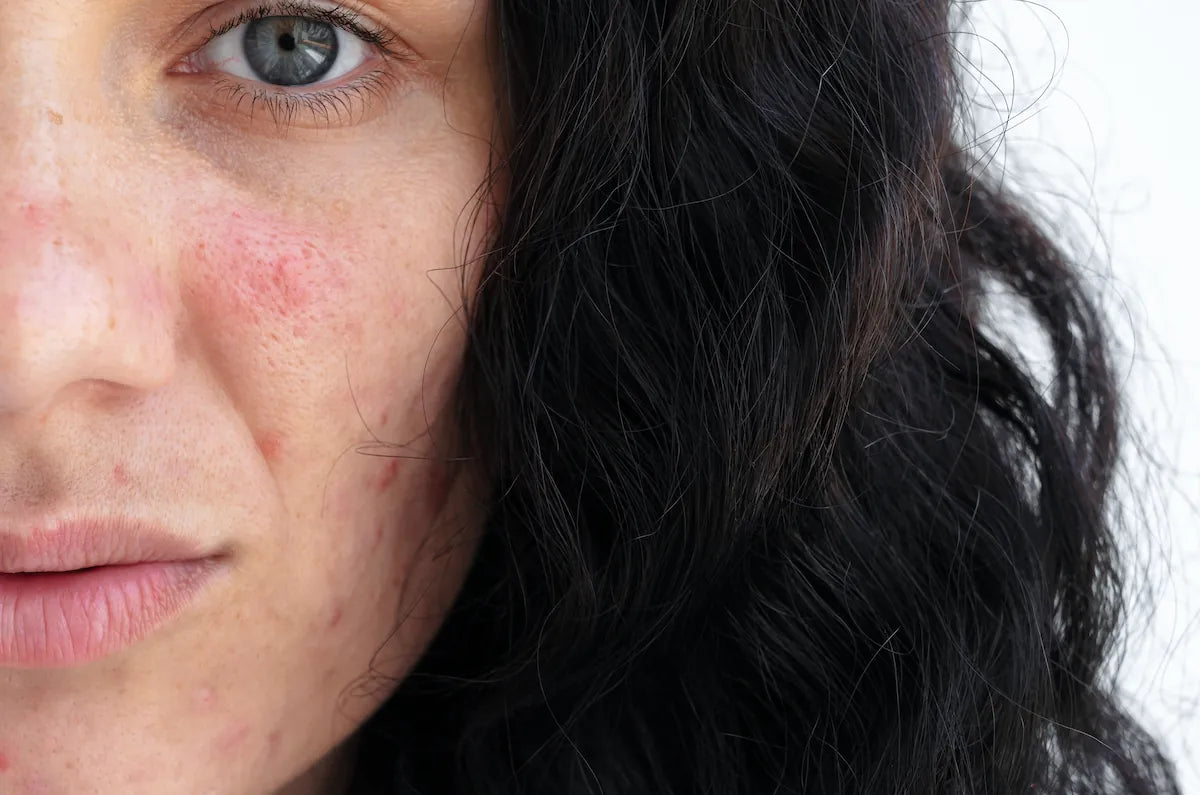
For those dealing with acne, retinaldehyde offers a gentler alternative to harsh acne treatment options. Its comedolytic properties help unclog pores by normalizing oil production and preventing the formation of new blemishes. The ingredient is particularly effective for mild to moderate acne, though it’s not typically the first-line treatment for severe acne.
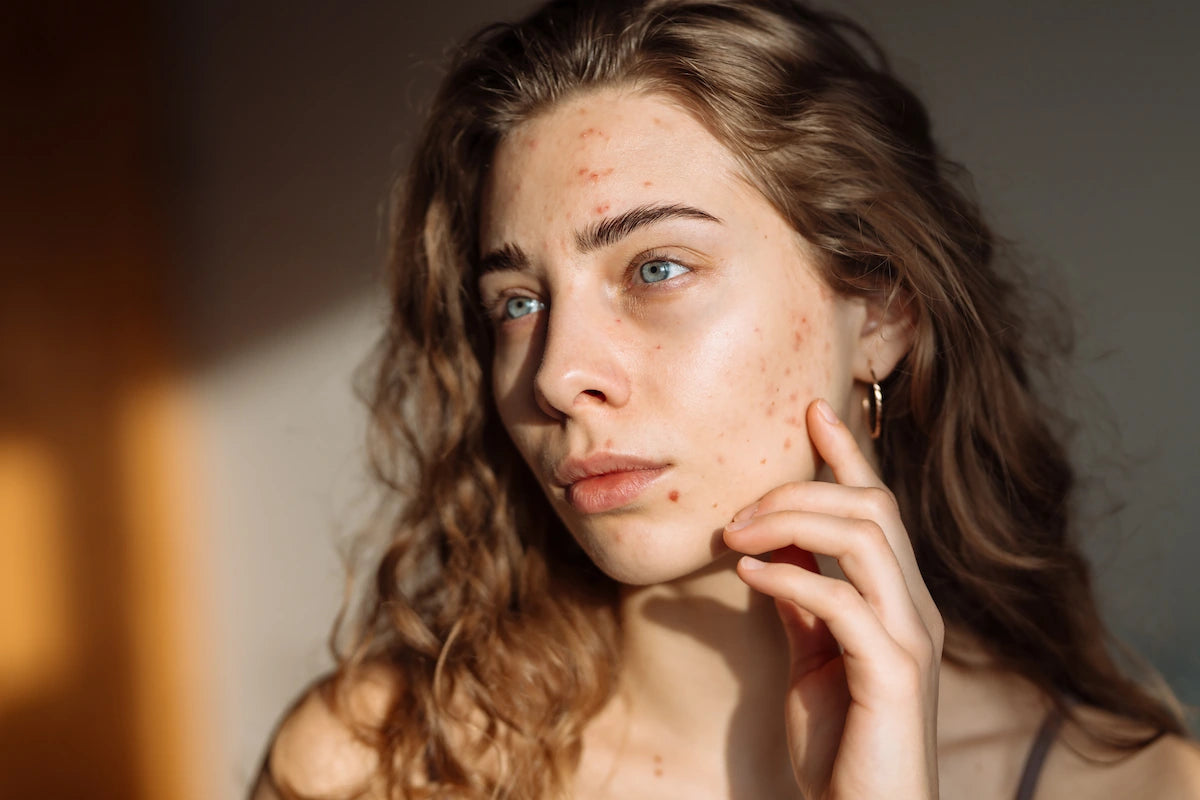

The anti-inflammatory effects also help reduce the redness and inflammation associated with active breakouts, while promoting faster healing that can minimize the appearance of acne scars over time.
Pigmentation and Uneven Skin Tone Improvement
Retinaldehyde excels at addressing various pigmentation concerns by regulating melanin synthesis. This makes it effective for fading age spots, dark spots, and post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation that often follows acne breakouts.
The ingredient’s ability to accelerate cell turnover means pigmented cells are shed more quickly, while new cells emerge with more even skin color distribution. This dual action makes retinaldehyde particularly valuable for addressing sun damage and age-related pigmentation changes.
Enhanced Skin Barrier Function
Beyond its anti-aging and acne benefits, retinaldehyde strengthens the skin barrier through improved keratinocyte function. This enhanced barrier reduces sensitivity, improves moisture retention, and provides better protection against environmental aggressors. Users often notice their skin becomes more resilient and less reactive to other ingredients, making it easier to incorporate additional skincare products without irritation.
Retinaldehyde vs Other Retinoids
Understanding how retinaldehyde compares to other retinoids helps you make informed decisions about which option best suits your skin needs and tolerance level. For those who find retinol too slow or need to use high concentrations that cause irritation, retinaldehyde provides a more efficient path to results. Retinol makes the skin more sensitive and prone to irritation, especially at higher strengths, which is why some people prefer retinaldehyde for its gentler profile and similar benefits.
Retinaldehyde vs Retinol
Retinol remains the most popular over-the-counter retinoid, but retinaldehyde offers several advantages. While retinol requires two conversion steps to become active, retinaldehyde needs only one, making it approximately 10 times more potent. This means you’ll typically see results faster with retinaldehyde than with comparable retinol product concentrations.
For those who find retinol too slow or need to use high concentrations that cause irritation, retinaldehyde provides a more efficient path to results. However, retinol may still be preferable for absolute beginners due to its widespread availability and extensive research history.
Retinaldehyde vs Tretinoin
Tretinoin represents the gold standard prescription retinoid, immediately bioactive without requiring conversion. However, this immediate activity often comes with significant skin irritation, including redness, peeling, and increased photosensitivity that can last for months.
Retinaldehyde offers many of tretinoin’s benefits with considerably less irritation, making it ideal for sensitive skin types or those who couldn’t tolerate prescription options. While tretinoin may ultimately provide more dramatic results for severe skin conditions, retinaldehyde delivers impressive improvements with greater comfort.
Comparison with Synthetic Retinoids
Third-generation synthetic retinoids like adapalene and tazarotene offer receptor selectivity that makes them particularly effective for specific conditions like acne. However, these prescriptions, only options often cause more irritation than retinaldehyde while being less versatile for general anti-aging concerns.
|
Retinoid Type |
Conversion Steps |
Potency Level |
Irritation Risk |
Availability |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Retinyl Esters |
3 steps |
Lowest |
Minimal |
OTC |
|
Retinol |
2 steps |
Low-Moderate |
Low |
OTC |
|
Retinaldehyde |
1 step |
Moderate-High |
Low-Moderate |
OTC |
|
Tretinoin |
0 steps |
High |
High |
Prescription |
|
Adapalene/Tazarotene |
0 steps |
High |
High |
Prescription |
How to Use Retinaldehyde Products
Successful retinaldehyde use requires a strategic approach that allows your skin to adapt while maximizing benefits. Following proper application techniques and building tolerance gradually will help you avoid common pitfalls that lead people to abandon retinoid use.
Getting Started
Begin with applications 2-3 times per week in the evening, applying retinaldehyde to clean, dry skin. Start with a pea-sized amount for your entire face, avoiding the immediate eye area initially. This conservative approach allows your skin to build tolerance over 4-6 weeks before increasing frequency.

The gradual introduction is crucial because even gentle retinoids can cause initial skin irritation as your cells adjust to increased turnover. Most people can progress to nightly use within 6-8 weeks, though some prefer to maintain every-other-night application long-term.
Application Tips and Best Practices
Proper application technique has a significant impact on both results and tolerability. After cleansing, wait for your skin to be completely dry before applying retinaldehyde, as damp skin increases absorption and potential irritation. Apply the product in gentle upward strokes, avoiding pulling or rubbing.
Layer your retinaldehyde under a moisturizer, rather than mixing them together, as this helps maintain the product’s stability and efficacy. If you experience dryness, consider using a hyaluronic acid serum before applying retinaldehyde, followed by a ceramide-rich moisturizer.
Avoid combining retinaldehyde with alpha hydroxy acids, beta hydroxy acids, or vitamin C initially, as these combinations can increase irritation. Once your skin has adapted (typically after 6-8 weeks), you may gradually introduce other actives on alternating nights.
Storage and Stability Considerations
Retinaldehyde’s effectiveness depends heavily on proper storage. Keep products in cool, dark environments away from direct sunlight, which can degrade the active ingredient. Many retinaldehyde formulations use specialized packaging or stabilizing technologies to maintain potency, but proper storage remains essential.
Check expiration dates carefully and note any changes in color or consistency, which may indicate degradation. Air-tight packaging helps preserve stability, so always replace caps securely after use.
Sun Protection Requirements
Like all topical retinoids, retinaldehyde increases photosensitivity, making diligent sun protection non-negotiable. Apply broad-spectrum sunscreen with SPF 30 or higher every morning, regardless of weather or planned activities. Consider sun protective clothing for extended outdoor exposure.
The photosensitizing effects aren’t just about preventing burns; UV exposure can also break down retinaldehyde and reduce its effectiveness. Consistent use of sunscreen protects both your skin and your investment in the best retinaldehyde products.
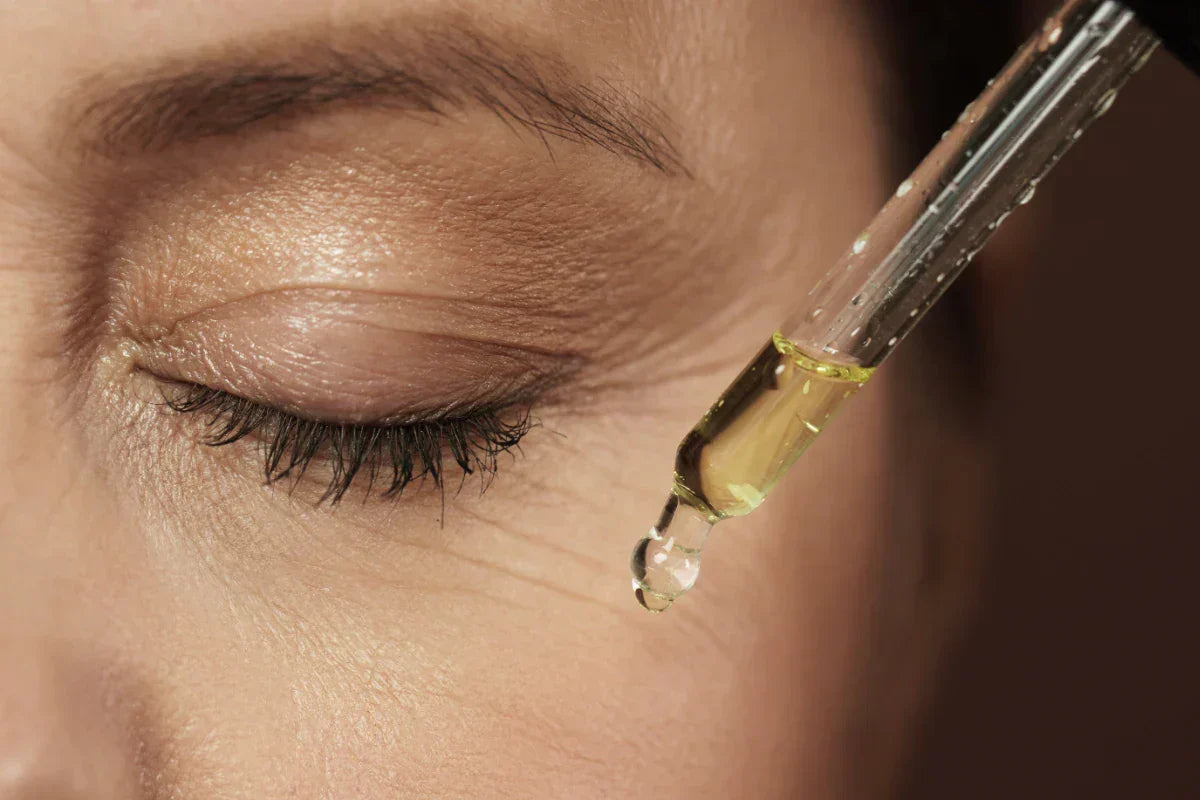
Choosing the Right Retinaldehyde Product
Selecting the ideal retinaldehyde product starts with understanding your unique skin needs and goals. If you have sensitive skin or are new to topical retinoids, opt for formulations with a lower concentration of retinaldehyde, typically around 0.05%. These gentler options help minimize the risk of skin irritation, redness, dryness, or peeling, making it easier to incorporate retinaldehyde into your routine without discomfort.
For those aiming to address more stubborn concerns, such as acne scars, uneven skin tone, or pronounced fine lines and wrinkles, a slightly higher concentration (up to 0.1%) may deliver more noticeable results. Retinaldehyde is available in various skin creams and serums, so consider your preferred texture and how it fits into your existing skincare regimen.
Always check the ingredient list to ensure the product is free from unnecessary fragrances or harsh additives that could trigger irritation. Follow the manufacturer’s instructions closely, starting with a small amount and gradually increasing as your skin builds tolerance. This approach helps you enjoy the benefits of retinaldehyde, smoother skin, fewer wrinkles, and a more even complexion, while minimizing the risk of adverse reactions.
Combining Retinaldehyde with Other Skincare Treatments
Maximizing the benefits of retinaldehyde often involves pairing it with complementary skincare treatments. For example, incorporating alpha hydroxy acids (AHAs) into your routine can further reduce fine lines and wrinkles and enhance overall skin texture by gently exfoliating dead skin cells. To counteract any dryness or sensitivity, layering a hyaluronic acid serum before your moisturizer can help lock in hydration and soothe the skin, making retinaldehyde more tolerable for those with sensitive skin.
When introducing new treatments alongside retinaldehyde, start with lower concentrations and increase gradually as your skin adapts. This slow approach helps prevent irritation and allows you to monitor how your skin responds to each ingredient.
Because retinaldehyde can make your skin more sensitive to sunlight, daily sun protection is essential. Always wear sunscreen with at least SPF 30, and consider sun protective clothing or seeking shade during peak hours to guard against further sun damage. By thoughtfully combining retinaldehyde with other treatments and prioritizing sun safety, you can achieve smoother texture, reduced wrinkles, and a healthier-looking complexion.
Choosing the Right Retinaldehyde Product
Selecting the ideal retinaldehyde product starts with understanding your unique skin needs and goals. If you have sensitive skin or are new to topical retinoids, opt for formulations with a lower concentration of retinaldehyde, typically around 0.05%. These gentler options help minimize the risk of skin irritation, redness, dryness, or peeling, making it easier to incorporate retinaldehyde into your routine without discomfort.
For those aiming to address more stubborn concerns, such as acne scars, uneven skin tone, or pronounced fine lines and wrinkles, a slightly higher concentration (up to 0.1%) may deliver more noticeable results. Retinaldehyde is available in a variety of skin creams and serums, so consider your preferred texture and how it fits into your existing regimen.
Always check the ingredient list to ensure the product is free from unnecessary fragrances or harsh additives that could trigger irritation. Follow the manufacturer’s instructions closely, starting with a small amount and gradually increasing as your skin builds tolerance. This approach helps you enjoy the benefits of retinaldehyde, like smoother skin, fewer wrinkles, and a more even complexion, while minimizing the risk of adverse reactions.

Combining Retinaldehyde with Other Skincare Treatments
Maximizing the benefits of retinaldehyde often involves pairing it with complementary skincare treatments. For example, incorporating alpha hydroxy acids (AHAs) into your routine can further reduce fine lines and wrinkles and enhance overall skin texture by gently exfoliating dead skin cells. To counteract any dryness or sensitivity, layering a hyaluronic acid serum before your moisturizer can help lock in hydration and soothe the skin, making retinaldehyde more tolerable for those with sensitive skin.
When introducing new treatments alongside retinaldehyde, start with lower concentrations and increase gradually as your skin adapts. This slow approach helps prevent irritation and allows you to monitor how your skin responds to each ingredient.
Because retinaldehyde can make your skin more sensitive to sunlight, daily sun protection is essential. Always wear sunscreen with at least SPF 30, and consider sun protective clothing or seeking shade during peak hours to guard against further sun damage. By thoughtfully combining retinaldehyde with other treatments and prioritizing sun safety, you can achieve smoother texture, reduced wrinkles, and a healthier-looking complexion.
Side Effects and Precautions
While retinaldehyde is generally well-tolerated compared to stronger retinoids, understanding potential side effects helps you use it safely and effectively. Most adverse reactions are mild and temporary, occurring primarily during the initial adaptation period.
Common Initial Reactions
The most frequent side effects include mild redness, dryness, and flaking during the first 2-4 weeks of use. This “retinoid adjustment period” is normal and typically resolves as your skin adapts to increased cell turnover. Some users also experience slight stinging upon application, which usually diminishes with continued use.
These reactions are generally less severe than those experienced with prescription retinoids or high-concentration retinol products. However, if irritation persists beyond 4-6 weeks or becomes severe, reduce application frequency or discontinue use temporarily.
Managing Sensitivity
For those with sensitive skin or rosacea, extra precautions can help minimize reactions. Start with once-weekly applications and increase frequency very gradually. Consider using a gentle, fragrance-free moisturizer both before and after retinaldehyde application to create a protective barrier.
If you experience persistent irritation, try applying retinaldehyde over a thin layer of moisturizer rather than directly to skin. This “buffering” technique reduces penetration slightly but can significantly improve tolerability for sensitive skin types.
Special Populations and Contraindications
Pregnant and breastfeeding women should consult healthcare providers before using retinaldehyde, as safety data in these populations remains limited. While topical retinoids are generally considered safer than oral forms, professional guidance ensures that appropriate decisions are made for individual circumstances.
Those with extremely sensitive skin conditions, active eczema, or compromised skin barriers should introduce retinaldehyde very cautiously or consider alternatives. Additionally, individuals using other prescription skincare treatments should consult their dermatologist about potential interactions.
Who Should Use Retinaldehyde
Retinaldehyde fills a unique niche in skincare, making it ideal for specific user profiles who want effective results without extreme measures. Understanding whether you’re a good candidate helps set appropriate expectations and achieve optimal outcomes.
Ideal Candidates
Adults in their late twenties to early thirties, beginning preventive anti-aging routines, represent prime candidates for retinaldehyde. At this age, early intervention can prevent significant collagen loss while building tolerance for potentially stronger treatments later if needed.
Those who have struggled with retinol’s slow results but want to avoid prescription retinoid side effects often find that retinaldehyde provides the perfect balance. Similarly, people with sensitive skin who couldn’t tolerate tretinoin may discover they can use retinaldehyde successfully.
Individuals dealing with mild acne, post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation, or early signs of aging benefit particularly well from retinaldehyde’s multi-faceted approach. The ingredient addresses multiple concerns simultaneously, making it efficient for comprehensive skin improvement.
When to Consider Alternatives
People with severe acne may need stronger prescription treatments for optimal results, though retinaldehyde can serve as excellent maintenance therapy once active breakouts are controlled. Similarly, those with advanced photoaging might require more aggressive interventions initially.
If you’re completely new to retinoids and have very sensitive skin, starting with lower-concentration retinol might be safer before progressing to retinaldehyde. Conversely, if you’ve successfully used retinol but want stronger results, jumping directly to prescription tretinoin might be more efficient than the intermediate step.
Skin Types and Conditions
Retinaldehyde works well across various skin types, though application approaches may vary. Oily skin typically tolerates retinaldehyde well and may benefit from its effects on regulating oil production. Individuals with dry skin types should prioritize moisturizing support and may require longer adjustment periods.
Combination skin often responds excellently to retinaldehyde’s pore-refining and texture-improving benefits. Those with mature skin appreciate the comprehensive anti-aging effects, while younger users value the preventive and acne-fighting properties.
Clinical Research and Effectiveness
The scientific evidence supporting the use of retinaldehyde provides confidence in its effectiveness and helps set realistic expectations for results. Multiple clinical studies have documented both short-term and long-term benefits across various skin concerns.
Anti-Aging Research
Clinical trials using 0.05% retinaldehyde concentrations consistently demonstrate measurable improvements in fine lines and skin texture within 12 weeks. These studies utilize objective measurement tools, such as profilometry and ultrasound, to quantify changes in skin thickness and elasticity.
Six-month studies reveal continued improvements, with participants showing increased epidermal thickness and enhanced dermal matrix organization. The research indicates that benefits continue to accumulate with longer use, making retinaldehyde an excellent long-term skincare investment.
Comparative studies highlight retinaldehyde’s superior vitamin A activity compared to retinol, with research indicating approximately 10 times greater bioactivity. This translates to faster visible results and the ability to use lower concentrations while achieving significant outcomes.
Acne and Pigmentation Studies
Research on retinaldehyde’s acne treatment potential shows promising results for mild to moderate cases. Studies have documented reduced comedone formation, decreased inflammation, and improved overall skin texture in participants with acne-prone skin.
Pigmentation research demonstrates retinaldehyde’s effectiveness for fading age spots and post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation. The ingredient’s ability to regulate melanin synthesis while promoting cell turnover creates a two-pronged approach to pigmentation correction.
Safety and Tolerability Data
Long-term safety studies confirm retinaldehyde’s favorable profile compared to stronger retinoids. Research participants report significantly lower rates of irritation, redness, and peeling compared to users of tretinoin, while still achieving substantial skin improvements.
The studies consistently show that most users can progress to nightly application within 4-8 weeks, with minimal long-term side effects. This tolerability profile makes retinaldehyde suitable for sustained use, which is crucial for maintaining anti-aging benefits.
Long-Term Effects of Retinaldehyde Use
With consistent use over a few months, retinaldehyde can deliver impressive long-term improvements in your skin’s appearance and health. Regular application helps refine skin texture, diminish the look of fine lines and wrinkles, and fade age spots, resulting in a more youthful and radiant complexion. One of the key benefits is the stimulation of collagen production, which enhances skin elasticity and firmness as you age.
Patience is important, while some changes may be visible within weeks, the most significant results often appear after several months of steady use. To minimize the risk of skin irritation, redness, dryness, or peeling, introduce retinaldehyde gradually into your skincare routine, starting with two to three times per week and increasing frequency as your skin becomes more resilient.

Sticking to a consistent routine not only maximizes the anti-aging effects of retinaldehyde but also helps maintain improvements in skin texture and tone over time. If you experience persistent irritation, consider adjusting your application frequency or consulting a skincare professional for personalized advice.
Expert Insights on Retinaldehyde
Experts in molecular biology and pure and applied chemistry recognize retinaldehyde as a powerful bioactive form of vitamin A, essential for maintaining healthy skin cells and supporting the skin’s natural renewal processes. As a precursor to retinoic acid, retinaldehyde delivers proven anti-aging benefits, helping to reduce the appearance of fine lines, wrinkles, and age spots while enhancing overall skin tone and texture.
When used in well-formulated skincare products, retinaldehyde not only enhances the appearance of the skin but also helps regulate oil production and reduce inflammation, making it suitable for a variety of skin types and concerns. However, because it's a potent ingredient, it’s essential to select the right product for your needs and follow the usage instructions carefully to avoid potential side effects, such as skin irritation, dryness, or redness.
For optimal results, consult with a dermatologist or skincare professional who can recommend the most suitable treatment plan tailored to your skin condition, age, and goals. With expert guidance and a thoughtful approach, retinaldehyde can be a valuable addition to your anti-aging and skin health regimen.
Long-Term Effects of Retinaldehyde Use
With consistent use over a few months, retinaldehyde can deliver impressive long-term improvements in your skin’s appearance and health. Regular application helps refine skin texture, diminish the look of fine lines and wrinkles, and fade age spots, resulting in a more youthful and radiant complexion. One of the key benefits is the stimulation of collagen production, which enhances skin elasticity and firmness as you age.
Patience is important, while some changes may be visible within weeks, the most significant results often appear after several months of steady use. To minimize the risk of skin irritation, redness, dryness, or peeling, introduce retinaldehyde gradually into your skincare routine, starting with two to three times per week and increasing frequency as your skin becomes more resilient.
Sticking to a consistent routine not only maximizes the anti-aging effects of retinaldehyde but also helps maintain improvements in skin texture and tone over time. If you experience persistent irritation, consider adjusting your application frequency or consulting a skincare professional for personalized advice.
Expert Insights on Retinaldehyde
Experts in molecular biology and pure and applied chemistry recognize retinaldehyde as a powerful bioactive form of vitamin A, essential for maintaining healthy skin cells and supporting the skin’s natural renewal processes. As a precursor to retinoic acid, retinaldehyde delivers proven anti-aging benefits, helping to reduce the appearance of fine lines, wrinkles, and age spots while enhancing overall skin tone and texture.
When used in well-formulated skincare products, retinaldehyde not only enhances the appearance of the skin but also helps regulate oil production and reduce inflammation, making it suitable for a variety of skin types and concerns. However, because it's a potent ingredient, it’s essential to select the right product for your needs and follow the usage instructions carefully to avoid potential side effects, such as skin irritation, dryness, or redness.
For best results, consult with a dermatologist or skincare professional who can recommend the most appropriate treatment plan based on your individual skin condition, age, and goals. With expert guidance and a thoughtful approach, retinaldehyde can be a valuable addition to your anti-aging and skin health regimen.
Conclusion
Retinaldehyde represents a significant advancement in accessible retinoid technology, offering the perfect balance between effectiveness and tolerability that many skincare enthusiasts have been seeking. Its unique position in the vitamin A conversion pathway provides faster results than retinol while maintaining gentleness that makes it suitable for sensitive skin types.
The comprehensive benefits, from reducing fine lines and wrinkles to treating acne and improving pigmentation, make retinaldehyde an excellent choice for those wanting a single ingredient that addresses multiple skin concerns. Clinical research supports its effectiveness, while real-world use confirms its superior tolerability compared to prescription alternatives.
Whether you’re starting your first anti-aging routine, seeking better acne treatment options, or looking to upgrade from slower-acting retinol, retinaldehyde deserves serious consideration. Its proven track record, combined with over-the-counter availability, makes it an accessible yet powerful tool for achieving healthier, more youthful-looking skin.
Consider incorporating retinaldehyde into your skincare routine if you’ve been hesitant about retinoids or want faster results than traditional retinol provides. With proper use and realistic expectations, this remarkable vitamin A derivative can help you achieve the complexion improvements you’ve been working toward.